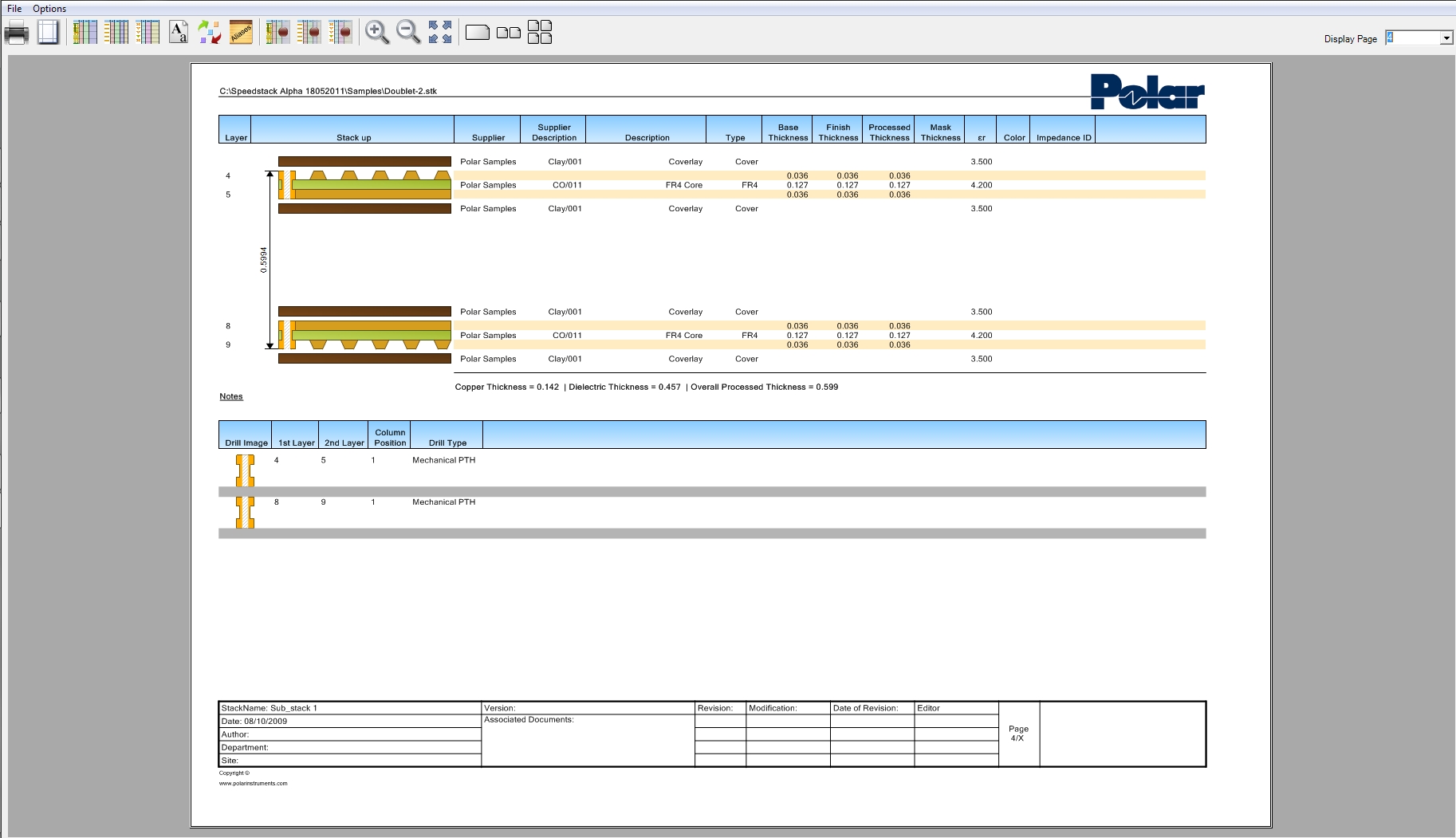
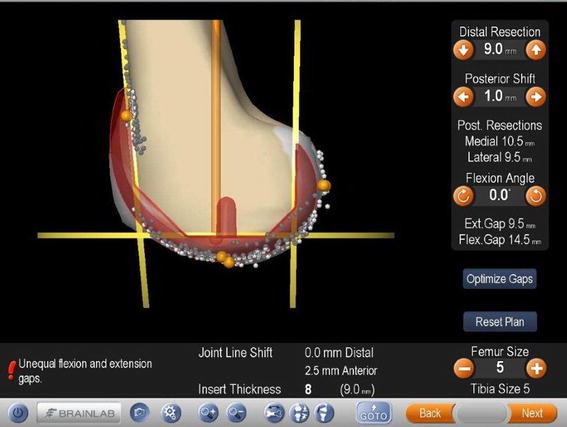
Navigation image of the femoral component planning. The size of

Download scientific diagram | Navigation image of the femoral component planning. The size of the component matches the individual model of this patient knee well. Femoral component is placed at 0° of flexion. Please notice that the flexion gap is 12 mm being 1.5 mm larger than the extension gap and hence showing unequal flexion and extension gaps. from publication: Intentional Femoral Component Flexion - A Method to Balance the Flexion-extension Gap in Navigated Total Knee Replacement | Introduction: Flexion of the femoral component has been described as a theoretical possibility to balance flexion and extension gap. Computer navigation has made it possible to intentionally flex the femoral component in a controlled fashion to take advantage of the | Knee, Navigation and Balance | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
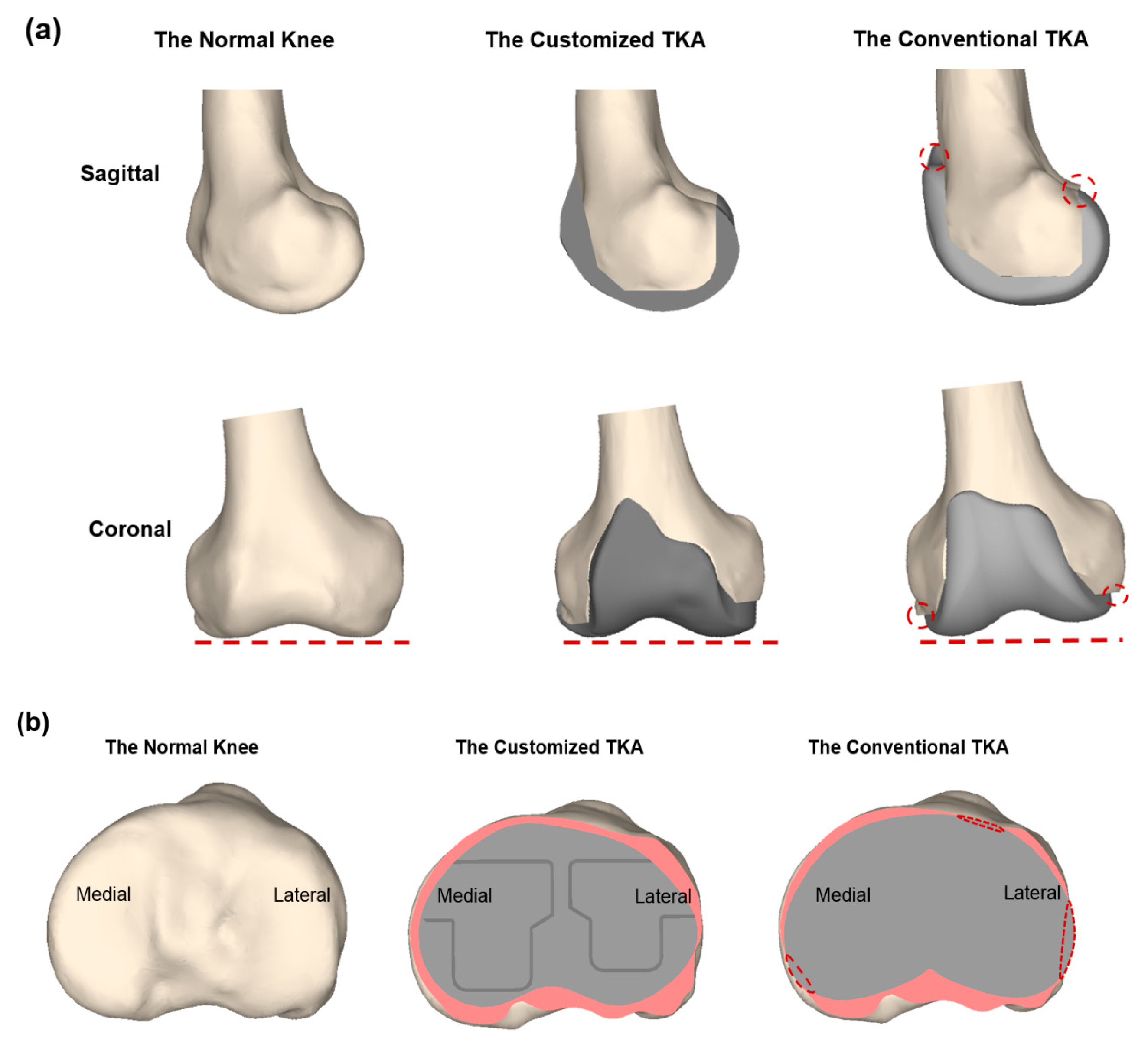
JCM, Free Full-Text

Notching is less, if femoral component sagittal positioning is planned perpendicular to distal femur anterior cortex axis, in navigated TKA, Knee Surgery & Related Research

A gap balancing technique for adjusting the component gap in total knee arthroplasty using a navigation system - ScienceDirect

Praveen GOVARDHAN, Junior resident, MS Ortho DNB Ortho

3D-CT: A better map for hip surgery - OPNews
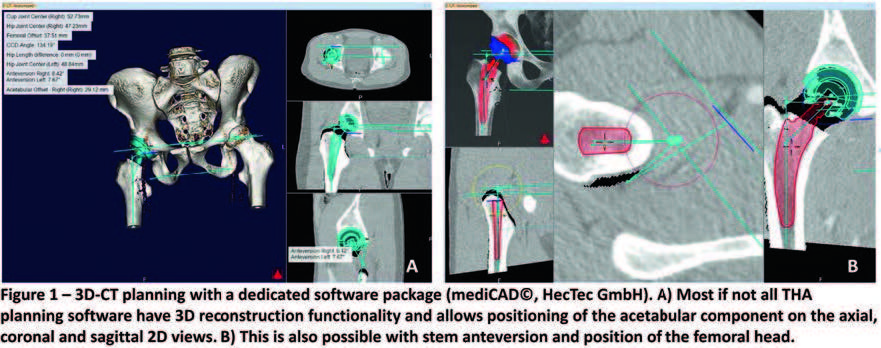
3D-CT: A better map for hip surgery - mediCAD
Processes, Free Full-Text

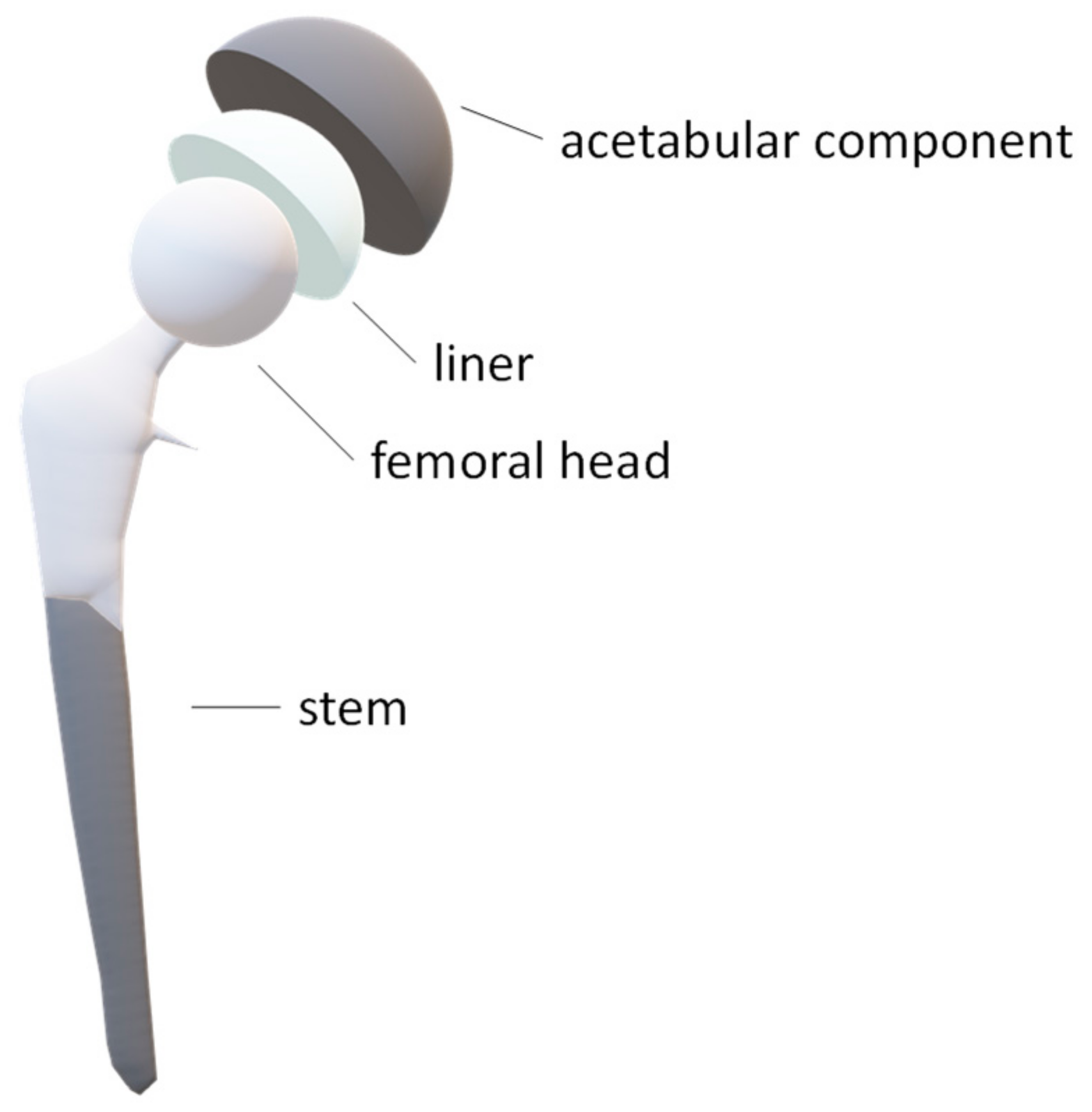
Combining the advantages of 3-D and 2-D templating of total hip arthroplasty using a new tin-filtered ultra-low-dose CT of the hip with comparable radiation dose to conventional radiographs
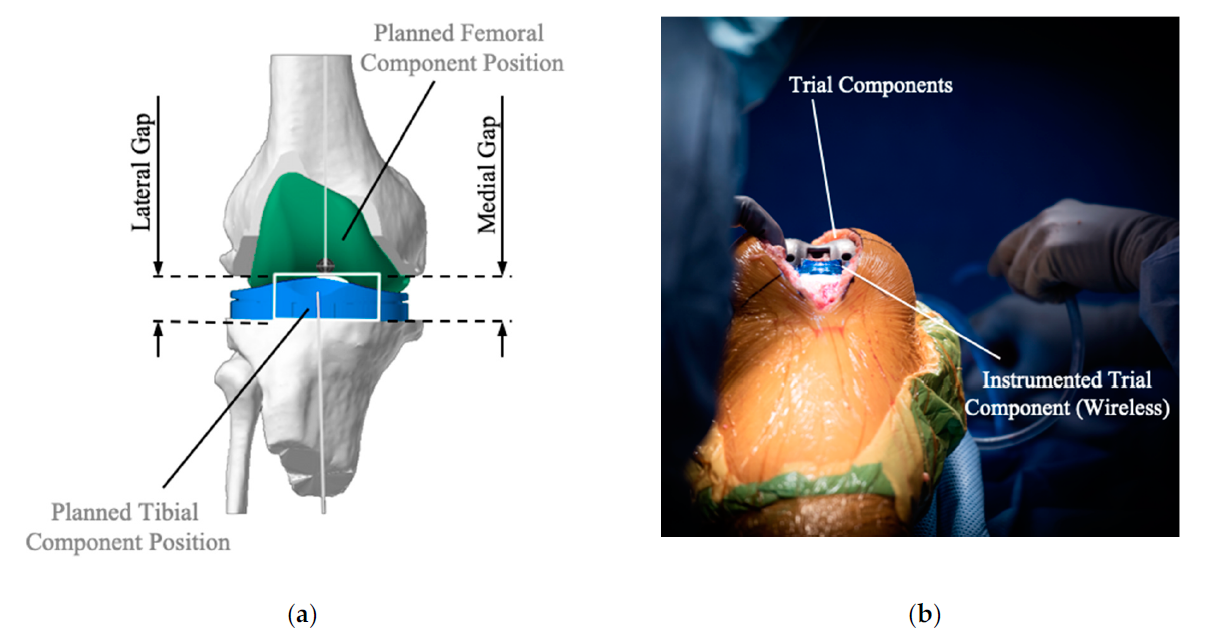
Sensors, Free Full-Text

PDF) Intentional Femoral Component Flexion - A Method to Balance

TKA Kinematic Alignment - Recon - Orthobullets